循环链表
from __future__ import annotations
from collections.abc import Iterator
from dataclasses import dataclass
from typing import Any
@dataclass
class Node:
data: Any
next_node: Node | None = None
@dataclass
class CircularLinkedList:
head: Node | None = None # Reference to the head (first node)
tail: Node | None = None # Reference to the tail (last node)
def __iter__(self) -> Iterator[Any]:
"""
Iterate through all nodes in the Circular Linked List yielding their data.
Yields:
The data of each node in the linked list.
"""
node = self.head
while node:
yield node.data
node = node.next_node
if node == self.head:
break
def __len__(self) -> int:
"""
Get the length (number of nodes) in the Circular Linked List.
"""
return sum(1 for _ in self)
def __repr__(self) -> str:
"""
Generate a string representation of the Circular Linked List.
Returns:
A string of the format "1->2->....->N".
"""
return "->".join(str(item) for item in iter(self))
def insert_tail(self, data: Any) -> None:
"""
Insert a node with the given data at the end of the Circular Linked List.
"""
self.insert_nth(len(self), data)
def insert_head(self, data: Any) -> None:
"""
Insert a node with the given data at the beginning of the Circular Linked List.
"""
self.insert_nth(0, data)
def insert_nth(self, index: int, data: Any) -> None:
"""
Insert the data of the node at the nth pos in the Circular Linked List.
Args:
index: The index at which the data should be inserted.
data: The data to be inserted.
Raises:
IndexError: If the index is out of range.
"""
if index < 0 or index > len(self):
raise IndexError("list index out of range.")
new_node: Node = Node(data)
if self.head is None:
new_node.next_node = new_node # First node points to itself
self.tail = self.head = new_node
elif index == 0: # Insert at the head
new_node.next_node = self.head
assert self.tail is not None # List is not empty, tail exists
self.head = self.tail.next_node = new_node
else:
temp: Node | None = self.head
for _ in range(index - 1):
assert temp is not None
temp = temp.next_node
assert temp is not None
new_node.next_node = temp.next_node
temp.next_node = new_node
if index == len(self) - 1: # Insert at the tail
self.tail = new_node
def delete_front(self) -> Any:
"""
Delete and return the data of the node at the front of the Circular Linked List.
Raises:
IndexError: If the list is empty.
"""
return self.delete_nth(0)
def delete_tail(self) -> Any:
"""
Delete and return the data of the node at the end of the Circular Linked List.
Returns:
Any: The data of the deleted node.
Raises:
IndexError: If the index is out of range.
"""
return self.delete_nth(len(self) - 1)
def delete_nth(self, index: int = 0) -> Any:
"""
Delete and return the data of the node at the nth pos in Circular Linked List.
Args:
index (int): The index of the node to be deleted. Defaults to 0.
Returns:
Any: The data of the deleted node.
Raises:
IndexError: If the index is out of range.
"""
if not 0 <= index < len(self):
raise IndexError("list index out of range.")
assert self.head is not None
assert self.tail is not None
delete_node: Node = self.head
if self.head == self.tail: # Just one node
self.head = self.tail = None
elif index == 0: # Delete head node
assert self.tail.next_node is not None
self.tail.next_node = self.tail.next_node.next_node
self.head = self.head.next_node
else:
temp: Node | None = self.head
for _ in range(index - 1):
assert temp is not None
temp = temp.next_node
assert temp is not None
assert temp.next_node is not None
delete_node = temp.next_node
temp.next_node = temp.next_node.next_node
if index == len(self) - 1: # Delete at tail
self.tail = temp
return delete_node.data
def is_empty(self) -> bool:
"""
Check if the Circular Linked List is empty.
Returns:
bool: True if the list is empty, False otherwise.
"""
return len(self) == 0
def test_circular_linked_list() -> None:
"""
Test cases for the CircularLinkedList class.
>>> test_circular_linked_list()
"""
circular_linked_list = CircularLinkedList()
assert len(circular_linked_list) == 0
assert circular_linked_list.is_empty() is True
assert str(circular_linked_list) == ""
try:
circular_linked_list.delete_front()
raise AssertionError # This should not happen
except IndexError:
assert True # This should happen
try:
circular_linked_list.delete_tail()
raise AssertionError # This should not happen
except IndexError:
assert True # This should happen
try:
circular_linked_list.delete_nth(-1)
raise AssertionError
except IndexError:
assert True
try:
circular_linked_list.delete_nth(0)
raise AssertionError
except IndexError:
assert True
assert circular_linked_list.is_empty() is True
for i in range(5):
assert len(circular_linked_list) == i
circular_linked_list.insert_nth(i, i + 1)
assert str(circular_linked_list) == "->".join(str(i) for i in range(1, 6))
circular_linked_list.insert_tail(6)
assert str(circular_linked_list) == "->".join(str(i) for i in range(1, 7))
circular_linked_list.insert_head(0)
assert str(circular_linked_list) == "->".join(str(i) for i in range(7))
assert circular_linked_list.delete_front() == 0
assert circular_linked_list.delete_tail() == 6
assert str(circular_linked_list) == "->".join(str(i) for i in range(1, 6))
assert circular_linked_list.delete_nth(2) == 3
circular_linked_list.insert_nth(2, 3)
assert str(circular_linked_list) == "->".join(str(i) for i in range(1, 6))
assert circular_linked_list.is_empty() is False
if __name__ == "__main__":
import doctest
doctest.testmod()
关于此算法
循环链表是由节点组成的端点连接的数据结构。与线性链表和双向链表类似,每个节点都由一个变量data组成,其中存储其内容,以及指向列表中下一个节点的指针。链表有一个指向相邻元素的pointer,但最后一个节点连接到头节点(即第一个节点本身),从而形成一个循环形状。
相对于数组、线性链表和双向链表的优势
- 任何节点都可以作为起点
- 适用于队列的实现
- 循环列表在需要重复遍历列表的应用程序中很有用
- 循环双向链表用于实现高级数据结构,如斐波那契堆。
- 链表的大小不是固定的(动态大小)
- 与数组相比,删除和添加元素的开销不大
缺点
- 与单向链表相比,循环链表更复杂。
- 与单向或双向链表相比,循环链表的反转更复杂。
- 如果遍历不当,可能会导致无限循环
- 与数组相比,元素只能顺序访问,不能随机访问
- 需要为连接链表中元素的指针进行额外的内存分配
时间复杂度
| 操作 | 平均 | 最坏 |
|---|---|---|
| 初始化 | O(1) | - |
| 访问 | O(n) | O(n) |
| 搜索 | O(n) | O(n) |
| 插入 | O(1) | O(n) |
| 删除 | O(1) | O(n) |
现实世界应用
- 将 CPU 分配给资源
- 多人棋盘游戏
SLL 与 CLL
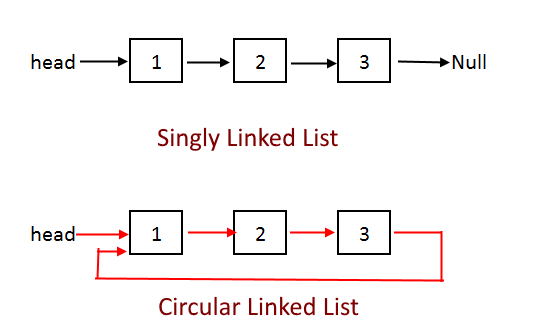
示例
插入
public void insertHead(int data)
{
Node temp = new Node(data);
Node cur = head;
while(cur.getNext() != head)
cur = cur.getNext();
if(head == null)
{
head = temp;
head.setNext(head);
}
else
{
temp.setNext(head);
head = temp;
cur.setNext(temp);
}
size++;
}