双向链表
"""
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Doubly_linked_list
"""
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.previous = None
self.next = None
def __str__(self):
return f"{self.data}"
class DoublyLinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
self.tail = None
def __iter__(self):
"""
>>> linked_list = DoublyLinkedList()
>>> linked_list.insert_at_head('b')
>>> linked_list.insert_at_head('a')
>>> linked_list.insert_at_tail('c')
>>> tuple(linked_list)
('a', 'b', 'c')
"""
node = self.head
while node:
yield node.data
node = node.next
def __str__(self):
"""
>>> linked_list = DoublyLinkedList()
>>> linked_list.insert_at_tail('a')
>>> linked_list.insert_at_tail('b')
>>> linked_list.insert_at_tail('c')
>>> str(linked_list)
'a->b->c'
"""
return "->".join([str(item) for item in self])
def __len__(self):
"""
>>> linked_list = DoublyLinkedList()
>>> for i in range(0, 5):
... linked_list.insert_at_nth(i, i + 1)
>>> len(linked_list) == 5
True
"""
return sum(1 for _ in self)
def insert_at_head(self, data):
self.insert_at_nth(0, data)
def insert_at_tail(self, data):
self.insert_at_nth(len(self), data)
def insert_at_nth(self, index: int, data):
"""
>>> linked_list = DoublyLinkedList()
>>> linked_list.insert_at_nth(-1, 666)
Traceback (most recent call last):
....
IndexError: list index out of range
>>> linked_list.insert_at_nth(1, 666)
Traceback (most recent call last):
....
IndexError: list index out of range
>>> linked_list.insert_at_nth(0, 2)
>>> linked_list.insert_at_nth(0, 1)
>>> linked_list.insert_at_nth(2, 4)
>>> linked_list.insert_at_nth(2, 3)
>>> str(linked_list)
'1->2->3->4'
>>> linked_list.insert_at_nth(5, 5)
Traceback (most recent call last):
....
IndexError: list index out of range
"""
length = len(self)
if not 0 <= index <= length:
raise IndexError("list index out of range")
new_node = Node(data)
if self.head is None:
self.head = self.tail = new_node
elif index == 0:
self.head.previous = new_node
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
elif index == length:
self.tail.next = new_node
new_node.previous = self.tail
self.tail = new_node
else:
temp = self.head
for _ in range(index):
temp = temp.next
temp.previous.next = new_node
new_node.previous = temp.previous
new_node.next = temp
temp.previous = new_node
def delete_head(self):
return self.delete_at_nth(0)
def delete_tail(self):
return self.delete_at_nth(len(self) - 1)
def delete_at_nth(self, index: int):
"""
>>> linked_list = DoublyLinkedList()
>>> linked_list.delete_at_nth(0)
Traceback (most recent call last):
....
IndexError: list index out of range
>>> for i in range(0, 5):
... linked_list.insert_at_nth(i, i + 1)
>>> linked_list.delete_at_nth(0) == 1
True
>>> linked_list.delete_at_nth(3) == 5
True
>>> linked_list.delete_at_nth(1) == 3
True
>>> str(linked_list)
'2->4'
>>> linked_list.delete_at_nth(2)
Traceback (most recent call last):
....
IndexError: list index out of range
"""
length = len(self)
if not 0 <= index <= length - 1:
raise IndexError("list index out of range")
delete_node = self.head # default first node
if length == 1:
self.head = self.tail = None
elif index == 0:
self.head = self.head.next
self.head.previous = None
elif index == length - 1:
delete_node = self.tail
self.tail = self.tail.previous
self.tail.next = None
else:
temp = self.head
for _ in range(index):
temp = temp.next
delete_node = temp
temp.next.previous = temp.previous
temp.previous.next = temp.next
return delete_node.data
def delete(self, data) -> str:
current = self.head
while current.data != data: # Find the position to delete
if current.next:
current = current.next
else: # We have reached the end an no value matches
raise ValueError("No data matching given value")
if current == self.head:
self.delete_head()
elif current == self.tail:
self.delete_tail()
else: # Before: 1 <--> 2(current) <--> 3
current.previous.next = current.next # 1 --> 3
current.next.previous = current.previous # 1 <--> 3
return data
def is_empty(self):
"""
>>> linked_list = DoublyLinkedList()
>>> linked_list.is_empty()
True
>>> linked_list.insert_at_tail(1)
>>> linked_list.is_empty()
False
"""
return len(self) == 0
def test_doubly_linked_list() -> None:
"""
>>> test_doubly_linked_list()
"""
linked_list = DoublyLinkedList()
assert linked_list.is_empty() is True
assert str(linked_list) == ""
try:
linked_list.delete_head()
raise AssertionError # This should not happen.
except IndexError:
assert True # This should happen.
try:
linked_list.delete_tail()
raise AssertionError # This should not happen.
except IndexError:
assert True # This should happen.
for i in range(10):
assert len(linked_list) == i
linked_list.insert_at_nth(i, i + 1)
assert str(linked_list) == "->".join(str(i) for i in range(1, 11))
linked_list.insert_at_head(0)
linked_list.insert_at_tail(11)
assert str(linked_list) == "->".join(str(i) for i in range(12))
assert linked_list.delete_head() == 0
assert linked_list.delete_at_nth(9) == 10
assert linked_list.delete_tail() == 11
assert len(linked_list) == 9
assert str(linked_list) == "->".join(str(i) for i in range(1, 10))
if __name__ == "__main__":
from doctest import testmod
testmod()
关于此算法
单向链表是一种线性、连接的数据结构,由节点组成。每个节点都包含一个名为 data 的变量,用来存储内容,以及指向链表中下一个节点的指针。链表有一个指向第一个节点的指针,也可能有一个指向最后一个节点的指针,以便更快地执行末尾操作。你也可以存储一个 length 变量来存储总长度。
**双向链表 (DLL)** 除了单向链表中存在的 next 指针和 data 之外,还包含一个额外的指针,通常称为 previous 指针。
相较于单向链表的优势
- 双向链表可以双向遍历。
- 如果给出要删除的节点的指针,则双向链表中的删除操作更有效率。
- 我们可以快速在给定节点之前插入新节点。
在单向链表中,要删除节点,需要指向前一个节点的指针。要获取这个前一个节点,有时需要遍历链表。在双向链表中,我们可以使用 previous 指针获取前一个节点。
相较于单向链表的劣势
- 双向链表的每个节点都需要为 previous 指针占用额外的空间。尽管可以通过单指针实现双向链表(参见此处和此处)。
- 所有操作都需要维护一个额外的 previous 指针。例如,在插入操作中,我们需要修改 previous 指针以及 next 指针。例如,在以下用于不同位置插入的函数中,我们需要 1 或 2 个额外的步骤来设置 previous 指针。
时间复杂度
| 操作 | 平均 | 最坏 |
|---|---|---|
| 访问 | Θ(n) | O(n) |
| 搜索 | Θ(n) | O(n) |
| 插入 | Θ(1) | O(1) |
| 删除 | Θ(1) | O(1) |
示例
class LinkedList {
Node head; // Pointer to the first element
Node tail; // Optional. Points to the last element
int length; // Optional
class Node {
int data; // Node data. Can be int, string, float, templates, etc
Node next; // Pointer to the next node on the list
Node prev;
Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
// Adding a node at the front of the list
public void push(int new_data) {
/* 1. allocate node
* 2. put in the data */
Node new_Node = new Node(new_data);
/* 3. Make next of new node as head and previous as NULL */
new_Node.next = head;
new_Node.prev = null;
/* 4. change prev of head node to new node */
if (head != null)
head.prev = new_Node;
/* 5. move the head to point to the new node */
head = new_Node;
}
/* Given a node as prev_node, insert a new node after the given node */
public void InsertAfter(Node prev_Node, int new_data) {
/*1. check if the given prev_node is NULL */
if (prev_Node == null) {
System.out.println("The given previous node cannot be NULL ");
return;
}
/* 2. allocate node
* 3. put in the data */
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
/* 4. Make next of new node as next of prev_node */
new_node.next = prev_Node.next;
/* 5. Make the next of prev_node as new_node */
prev_Node.next = new_node;
/* 6. Make prev_node as previous of new_node */
new_node.prev = prev_Node;
/* 7. Change previous of new_node's next node */
if (new_node.next != null)
new_node.next.prev = new_node;
}
}
在开头添加节点
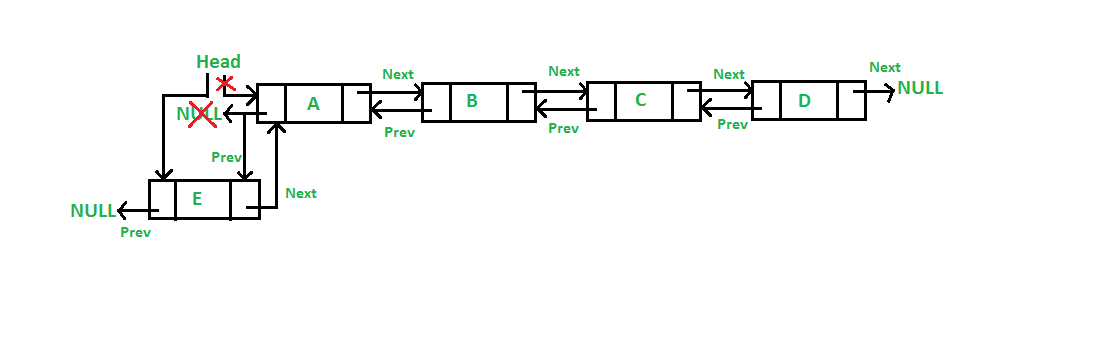
在给定节点之后添加节点
